Can a single antibody redefine treatment for a stubborn skin condition?
Story Overview
- Ligelizumab re-treatment offers sustainable symptom control in chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU).
- Over 50% of patients achieve significant improvement within 12 weeks.
- Higher IgE affinity distinguishes ligelizumab from other treatments.
- Long-term safety and efficacy confirmed in recent studies.
Understanding Ligelizumab and Its Role in Urticaria
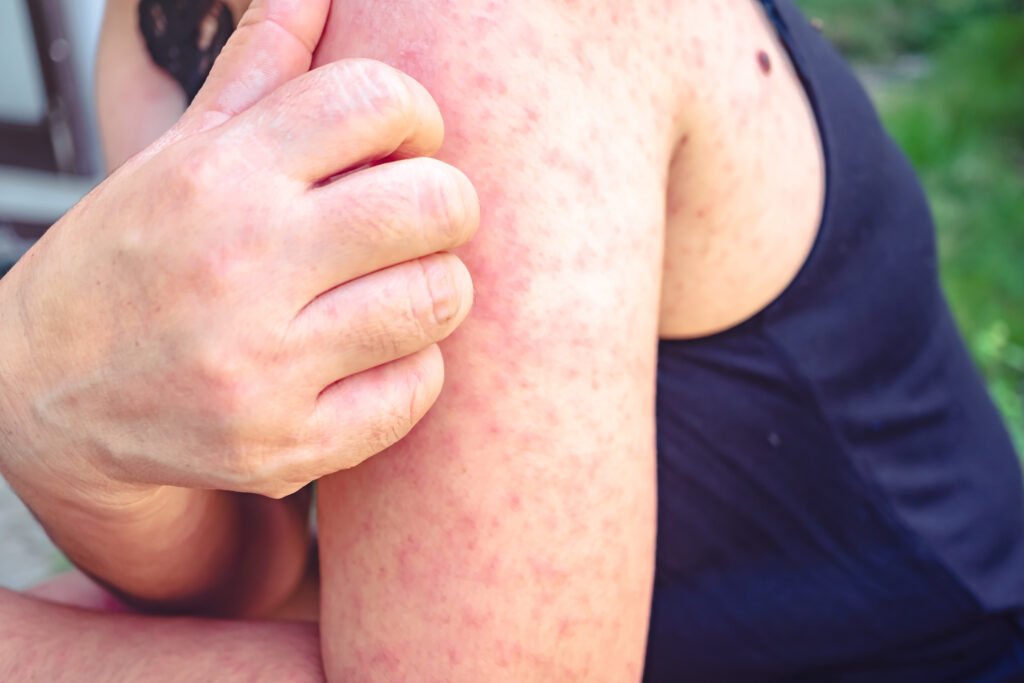
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is a persistent skin condition marked by recurring hives and itching, often resistant to standard antihistamine treatments. For many patients, finding effective relief poses a significant challenge. Ligelizumab, a monoclonal anti-IgE antibody developed by Novartis, emerges as a promising alternative, particularly for those who haven’t responded to omalizumab. With its higher IgE binding affinity, ligelizumab is now being hailed as a potential game-changer in CSU management.
Clinical trials have highlighted ligelizumab’s superior efficacy compared to placebo and its comparability to omalizumab in patients who do not respond to H1-antihistamines. The re-treatment studies have shown that patients maintained symptom control over extended periods, with a significant portion achieving a UAS7 score of 6 or lower, indicating minimal disease activity. Such outcomes offer renewed hope for those grappling with the daily discomfort of CSU.
Got a health question? Ask our AI doctor instantly, it’s free.
Clinical Trials and Meta-Analysis Insights
Ligelizumab’s journey from development to clinical trials has been meticulously documented. The Phase III trials, which began in 2018, involved a robust double-blind study comparing ligelizumab to omalizumab and placebo over 52 weeks. These trials have been instrumental in demonstrating ligelizumab’s capacity for long-term symptom management. Researchers have pooled data from multiple randomized controlled trials to conduct a comprehensive meta-analysis, further validating its efficacy and safety.
Watch;
The meta-analysis, which included 2,488 patients, highlighted the dose-dependent benefits of ligelizumab, with doses greater than 72 mg showing optimal results. It also noted fewer injection site reactions compared to omalizumab, a factor that could improve patient adherence and overall treatment satisfaction.
Stakeholder Dynamics and Market Implications
Numerous stakeholders have vested interests in the success of ligelizumab. Novartis, the pharmaceutical giant behind its development, aims to expand its pipeline beyond omalizumab, potentially capturing a significant share of the anti-IgE market. Clinical researchers and authors of recent studies are eager to validate ligelizumab’s role in treatment guidelines, while regulators like the FDA and EMA ensure the therapy’s safety and efficacy before approval.
Patients, the ultimate beneficiaries, seek symptom relief and improved quality of life, making them key players in this equation. The broader industry impact includes potential shifts in the biologics market, with ligelizumab setting new benchmarks for efficacy and tolerability.
Meet My Healthy Doc – instant answers, anytime, anywhere.
Current Developments and Future Outlook
Recent publications affirm the long-term viability of ligelizumab re-treatment. By April 2025, studies confirmed its effectiveness in reducing itch severity and overall disease activity compared to placebo. The sustained symptom control post-re-treatment supports its use as a chronic therapy option, potentially reducing the frequency of dosing due to its higher affinity for IgE.
As ligelizumab moves closer to broader clinical adoption, experts caution about evidence gaps in high-dose outcomes. However, the general consensus remains optimistic, with ligelizumab poised to redefine CSU management. The treatment’s market potential exceeds $1 billion, underscoring its economic impact and the promise it holds for countless patients worldwide.
Your instant doctor companion – online 24 hours a day.